This page describes how to interact via HUAWEI FreeBuds 4i via BT RFCOMM. It can be useful if you’re developing your own application to replace AI Life. The same content is actual for HONOR EarBuds 2 Lite.
All data was collected via reverse-engineering HUAWEI’s AudioAssistant android app. Also this post uses some information from TheLastGimbus’s research notes, like checksum algorithm name.
Device validation
HUAWEI’s BT-headphones uses a SPP (Serial Port Protocol) to communicate with official mobile app. In a nutshell, it’s a simple Bluetooth RFCOMM socket, which can be accessed from any OS and any programming language. On my device that service works on port 16.
But, in a good way, you should in first check that device has this communication protocol via SDP (Bluetooth Service Discover Protocol) via their UUID: 00001101-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb. If device supports SPP, you’ll got a port number associated with that UUID. Most common programming languages should have a ready-to-use library to perform that request. If not, you can just hard-code RFCOMM connection to port 16, it should work in most cases.
In python3, that can be done with:
import bluetooth
SPP_SERVICE_UUID = "00001101-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb"
DEVICE_ADDR = "xx:xx:xx:xx:xx" # Replace with your device MAC addr
services = bluetooth.find_service(address=DEVICE_ADDR, uuid=SPP_SERVICE_UUID)
first_match = services[0]
print(f"Found control protocol on {first_match['host']}, port={first_match['port']}")
If your device really supports SPP protocol, you’ll got output like: Found control protocol on xx:xx:xx:xx:xx, port=16. A good way is add this check into your application, to prevent communicating with non-supported devices. After that, you can simply connect to your device using this port number.
Package structure
Inside HUAWEI, this protocol is named MDN. I don’t know what it means, so I’ll just name it device control protocol, or SPP (Serial Port Protocol), which is more relevant.
Each data that you will send to device or got will have these structure. Please note field names, it will be used in this documentation. Offset from package start and length is presented in bytes.
| Offset |
Length |
Field name |
Description |
| 0 |
1 |
Constant |
Constant value 0x5a (ASCII Z, integer 90) |
| 1 |
2 |
Data length
(byte order: big) |
Length of parameters + 3 |
| 3 |
1 |
Constant |
Constant zero (0x00) |
| 4 |
2 |
Command type |
Two bytes, describing what action do you want to perform. In app logs, first is named ServiceID, second CommandID. I’ll just make to constant for any command. |
| 6 |
varies |
Parameters |
Command parameters in Type-Length-Value schema, see table bellow. Each command has their own set of parameters. |
| varies |
2 |
Checksum |
CTC16-Xmodem checksum of all bytes before this two
(thanks to TheLastGimbus, in HUAWEI app it was named just crc16, and realized with a very big array of precalculated data) |
As said, command parameters are encoded in TLV schema. So, each parameter look like:
| Offset |
Length |
Description |
| 0 |
1 |
Type, eg. parameter number |
| 1 |
1 |
Length, count of bytes in value |
| 2 |
varies |
Value, parameter value bytes |
If command has multiple parameters, it will be listed one after one.
Example package (in HEX):
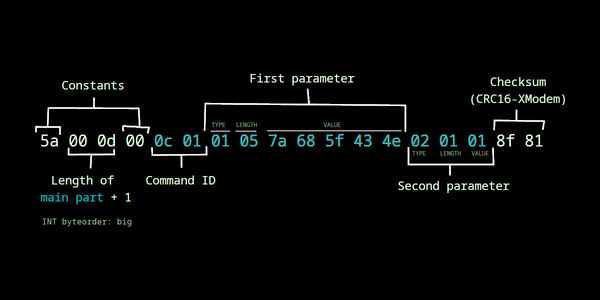
Based on that, there’s two major parts for any package: their command ID and list of their parameters.
Big part of this page is a list of available commands and their parameters. And, in code, you should realize some function or class that will build them to a set of bytes and send to device. Also, to fetch information from device, you should parse set of bytes from them to extract command ID and parameters that have been send to your application.
Playground
For simpler testing of command in this reference, I’ve created a simple Python script, that allows you manually interact with your device. This script defines Package class that can build or parse SPP package with structure, defined above. And it can send\receive that packages to\from your FreeBuds 4i, which allows you to build and send test packages directly from console. This will make testing of any command very simple.
To run them, you’ll need Python 3.10 or newer with pybluez package (pip install pybluez-edge). Download script here (GitHub Gist), and change device address in line 9. Now, run that script (OpenFreebuds must be closed, headset should be connected to your PC). It will connect to your device and give you an interactive Python prompt:
(venv) 9 23:27:08 [~/Projects/MyScripts/HuaweiPlayground] master
$ python main.py
Found service at port 16
Trying to connect...
OK
>>>
Here you can get packages from your device, and build & send your own. For example, this command will enable noise cancellation:
>>> Package(b"\x2b\x04", [
(1, 2),
]).send()
Pacakge — Class that implements SPP Package with structure described in previous section;- First parameter —
b"\x2b\x04" — command ID, two bytes, in that example (HEX 2B04) will change noise cancellation mode;
- Second parameter — list of command parameters, each parameter is presented as turtle
(type, value), where value can be byte-string (like first parameter) or integer (one-byte parameters only).
A bit more extended example, and this thing you can’t do from official app:
>>> Package(b"\x0C\x01", [
(1, b"en-GB"),
(2, 1),
]).send()
That command will change device language to English. You can also change it to Chinese, just replace en-GB with zh-CN. I prefer Chinese translation because their phrases are shorten and play faster =).
Device info & state
That section describes commands, that allow you to get information about current device, their battery level and in-ear state.
Fetch device info
Request: To fetch base information about device, you should send package with command ID 0107 with any parameters. Fun fact: official app sends a couple of empty parameters, but this isn’t required, device will response to empty package too.
| GET device info |
Length |
Value (Description) |
| Command ID |
2 |
Constant HEX 0107 (1, 7) |
In playground, you can send that via Package(b"\x01\x07", []).send().
Response: After sending 0107 command, device will send back that response:
| Device info bundle |
Length |
Value (Description) |
| Command ID |
2 |
Constant HEX 0107 (1, 7) |
| Parameter 2 |
2 |
?? |
| Parameter 3 |
varies |
Hardware version |
| Parameter 7 |
varies |
Firmware version |
| Parameter 9 |
varies |
Device S\N |
| Parameter 10 |
varies |
Device model |
| Parameter 15 |
varies |
Device model (shorter?) |
| Parameter 24 |
varies |
?? (looks like another S/N, official app don’t parse this) |
| Parameter 25 |
1 |
Some byte, always 1 |
Fetch battery info
Request: To get current battery level, build and send command with ID 0108.
| GET battery |
Length |
Value (Description) |
| Command ID |
2 |
Constant HEX 0108 (1, 8) |
Playground example: Package(b"\x01\x08", []).send().
Response: After that, you’ll got package like this. And the same package device will send if battery state will change while socket is connected.
| Battery state |
Length |
Value (Description) |
| Command ID |
2 |
0108 (1, 8) — Response for request above;
0127 (1, 39) — Battery changed notification |
| Parameter 1 |
1 |
Lowest battery value, looks like kept for old app versions |
| Parameter 2 |
3 |
Battery level for
left headphone in first byte,
right headphone in second byte,
case in third byte |
| Parameter 3 |
3 |
Charging state for headphones and case, three bytes in the same order as in parameter 2. 0 — not charging, 1 — charging |
In-ear state
This package describe current headphone state, is left\right put in ear or not,
Request: N\A
Response: Headphones drop that package when you put in\out it into ear.
| In-ear state |
Length |
Value (Description) |
| Command ID |
2 |
Constant HEX 2B03 (43, 3) |
| Parameter 8 |
1 |
New in-ear state for left headphone (may not exist)
1 — in, 0 — out |
| Parameter 9 |
1 |
New in-ear state for right headphone (may not exist)
1 — in, 0 — out |
Base commands
In that section I’ll describe base commands that you can use to read\write device status and main settings.
Noise-cancellation
Request: If you want to request current ANC mode, send command ID 2B2A.
| GET current mode |
Length |
Value (Description) |
| Command ID |
2 |
Constant HEX 2B2A (43, 42) |
Playground example: Package(b"\x2b\x2a", []).send().
Response/State: When you send that command, or ANC mode was changed with button on device, you’ll got a incoming package like that:
| Current ANC mode |
Length |
Value (Description) |
| Command ID |
2 |
Constant HEX 2B2A (43, 42) |
| Parameter 1 |
2 |
First byte unknown, looks like it didn’t do anything in that headphones model;
Second — current ANC mode, 0 — Normal, 1 — Noise cancellation, 2 — Awareness |
Write: To change ANC mode, build and send this package:
| Change ANC mode |
Length |
Value (Description) |
| Command ID |
2 |
Constant HEX 2B04 (43, 4) |
| Parameter 1 |
1 |
New ANC mode, integer
0 — Normal, 1 — Noise cancellation, 2 — Awareness |
Playground example: Package(b"\x2b\x04", [(1, NEW_MODE)]).send(), where NEW_MODE should be 0, 1 or 2.
Pause when plug out option
Request: To get current setting value, send that package.
| GET auto-pause |
Length |
Value (Description) |
| Command ID |
2 |
Constant HEX 2B11 (43, 17) |
Playground example: Package(b"\x2b\x11", []).send().
Response:
| Response auto-pause |
Length |
Value (Description) |
| Command ID |
2 |
Constant HEX 2B11 (43, 17) |
| Parameter 1 |
1 |
1 — enabled, 0 —disabled |
Write: To change this option, send that package:
| Response auto-pause |
Length |
Value (Description) |
| Command ID |
2 |
Constant HEX 2B10 (43, 16) |
| Parameter 1 |
1 |
New config value:
1 — enabled, 0 —disabled: |
Playground: Package(b"\x2b\x10", [(1, NEW_VALUE)]).send() where NEW_VALUE is 0 or 1.
Double-tap action option
Request: To fetch current option value, send package with command ID 0120.
| GET double-tap |
Length |
Value (Description) |
| Command ID |
2 |
Constant HEX 0120 (1, 32) |
Playground: Package(b"\x01\x20", []).send().
Response:
| Double-tap opt value |
Length |
Value (Description) |
| Command ID |
2 |
Constant HEX 0120 (1, 32) |
| Parameter 1 |
1 |
Signed integer, double tap action for left headphone (check table bellow for value description) |
| Parameter 2 |
1 |
Signed integer, double tap action for right headphone (check table bellow for value description) |
| Parameter 3 |
5 |
?? |
Write: To change this option, send package with command ID 011f, and place new option value to parameters 1 or 2 for left or right headphones. NOTE: only one parameter can be preset at once, you can’t change double-tap action for two headphones with one request.
| Set double-tap act |
Length |
Value (Description) |
| Command ID |
2 |
Constant HEX 011f (1, 31) |
| Parameter 1 |
1 |
Signed integer, double tap action for left headphone (check table bellow for value description) |
| Parameter 2 |
1 |
Signed integer, double tap action for right headphone (check table bellow for value description) |
Playground: Package(b"\x01\x1f", [(HEADPHONE_ID, NEW_VALUE),]).send() where HEADPHONE_ID should be 1 or 2 (left or right) and NEW_VALUE should be from table below.
Available options:
| Value |
Description |
| -1 |
Do nothing |
| 0 |
Voice assistant |
| 1 |
Pause/resume music |
| 2 |
Next track |
| 7 |
Previous track |
Long tap action option
Request: To fetch current option value, send package with command ID 2B17.
| GET long-tap |
Length |
Value (Description) |
| Command ID |
2 |
Constant HEX 2B17 (43, 23) |
Playground: Package(b"\x2b\x17", []).send().
Response:
| Long-tap opt value |
Length |
Value (Description) |
| Command ID |
2 |
Constant HEX 2B17 (43, 23) |
| Parameter 1 |
1 |
Signed integer, long tap action for left headphone (check table bellow for value description) |
| Parameter 2 |
1 |
Signed integer, long tap action for right headphone (check table bellow for value description) |
| Parameter 3 |
5 |
?? |
Write: All as in double-tap action, one parameter with one value. Command ID is 2b16. But… If you think that you can set different modes for different headphones, no, you can’t. When you change one option, device will copy them to other headphone.
| Set double-tap act |
Length |
Value (Description) |
| Command ID |
2 |
Constant HEX 2b16 (43, 22) |
| Parameter 1 |
1 |
Signed integer, double tap action for left headphone (check table bellow for value description) |
| Parameter 2 |
1 |
Signed integer, double tap action for right headphone (check table bellow for value description) |
Playground: Package(b"\x2b\x16", [(1, NEW_VALUE),]).send() where NEW_VALUE should be from table below.
Available options: (maybe device support more options, but I don’t checked)
| Value |
Description |
| -1 |
Do nothing |
| 10 |
Switch ANC modes in user-preferred order (see next paragraph |
Preferred ANC modes option
When long-tap is enabled, device will cycle through selected ANC modes. And this commands allow you to change that modes. I don’t know way developers made an extra option for that configuration, but that how it is.
Request: To fetch currently selected ANC modes, send package with command ID 2b19.
| GET ANC list |
Length |
Value (Description) |
| Command ID |
2 |
Constant HEX 2b19 (43, 25) |
Playground: Package(b"\x2b\x19", []).send().
Response:
| Long-tap opt value |
Length |
Value (Description) |
| Command ID |
2 |
Constant HEX 2b19 (43, 25) |
| Parameter 1 |
1 |
Signed integer, preferred ANC’s for left headphone (check table bellow for value description) |
| Parameter 2 |
1 |
Signed integer, preferred ANC’s for right headphone (check table bellow for value description) |
| Parameter 3 |
11 |
?? (ordered integers from 1 to 10, idk why they are here) |
Write: All the same as in long-tap configuration write, only command ID another: 2b18.
| Set double-tap act |
Length |
Value (Description) |
| Command ID |
2 |
Constant HEX 2b18 (43, 24) |
| Parameter 1 |
1 |
Signed integer, long tap action for left headphone (check table bellow for value description) |
| Parameter 2 |
1 |
Signed integer, long tap action for right headphone (check table bellow for value description) |
Playground: Package(b"\x2b\x18", [(1, NEW_VALUE),]).send() where NEW_VALUE should be from table below.
Available options:
| Value |
Description |
| 1 |
Disable ANC and noise cancellation |
| 2 |
Cycle all ANC modes |
| 3 |
Noise cancellation and awareness |
| 4 |
Disable ANC and awareness |
Extras
This features works on our device, but isn’t available in official apps directly. I found them into sources.
Device logs
Sometime, when sound isn’t playing, device start sending their logs in that structure:
| Logs |
Length |
Value (Description) |
| Command ID |
2 |
Constant HEX 0a0d (10, 13) |
| Parameter 1 |
1 |
Looks like always 3 |
| Parameter 2 |
4 |
Looks like some event ID |
| Parameter 4 |
varies |
JSON-encoded data as ASCII string |
My attempt to decode that didn’t success, so I can only give advice to ignore that packages.
Voice language
Request: This command will ask headphones for a list of available voice languages. Unfortunately, there’s no way to get current enabled language.
| GET languages |
Length |
Value (Description) |
| Command ID |
2 |
Constant HEX 0C02 (12, 2) |
Playground: Package(b"\x0c\x02", []).send().
Response:
| Langs list |
Length |
Value (Description) |
| Command ID |
2 |
Constant HEX 0C02 (12, 2) |
| Parameter 3 |
varies |
Comma-separated list of available locale options, example: en-GH,zh-CN. |
| Parameter 4 |
1 |
?? |
Write: To change current language, send package with command ID 0C01 in that struct:
| Change lang |
Length |
Value (Description) |
| Command ID |
2 |
Constant HEX 0C01 (12, 1) |
| Parameter 1 |
5 |
New language from list of available, example zh-CN |
| Parameter 2 |
1 |
Constant 1, idk why, but without that it won’t work |
Playground: Package(b"\x0c\x01", [(1, b"zh-CN"), (2, 1)]).send().
Unavailable in this reference
- I don’t research firmware update commands due to risk to brick my device. And as I know, all official firmware builds are signed, and device anyway won’t load customs. So, there’s no need to research that, for me;
